Botswana's geography
Borders of Botswanas
Botswana is a landlocked country located in the southern part of Africa. Botswana has an area of 581730 km².
Botswana has borders with the following states: Namibia to the west and north (1.544 km), Zambia (0.15 km), Zimbabwe in the north-east (834 km) and South Africa to the southeast and south (1.969 km). Remarkable is the border rectangle or quadripoint (where four countries meet) which is unique worldwide. It actually consists of two border triangles, located in close proximity of each other. One is the border triangle of Botswana – Namibia-Zambia and the other one – only 100 meters away – is Zambia-Botswana-Zimbabwe. However, the course of the border is disputed so one speaks of a virtual quadripoint.
The majority of Botswana lies at an altitude of about 1000 m to 1100 m. This huge plain forms the center of the Kalahari Basin and is essentially characterized by semi-arid grass, shrub and tree savannah landscapes. In Botswana, there are hardly any mountains, the whole country is very flat. Botswana's largest mountain is Monalanong Hill (1494m) south of Gaborone.
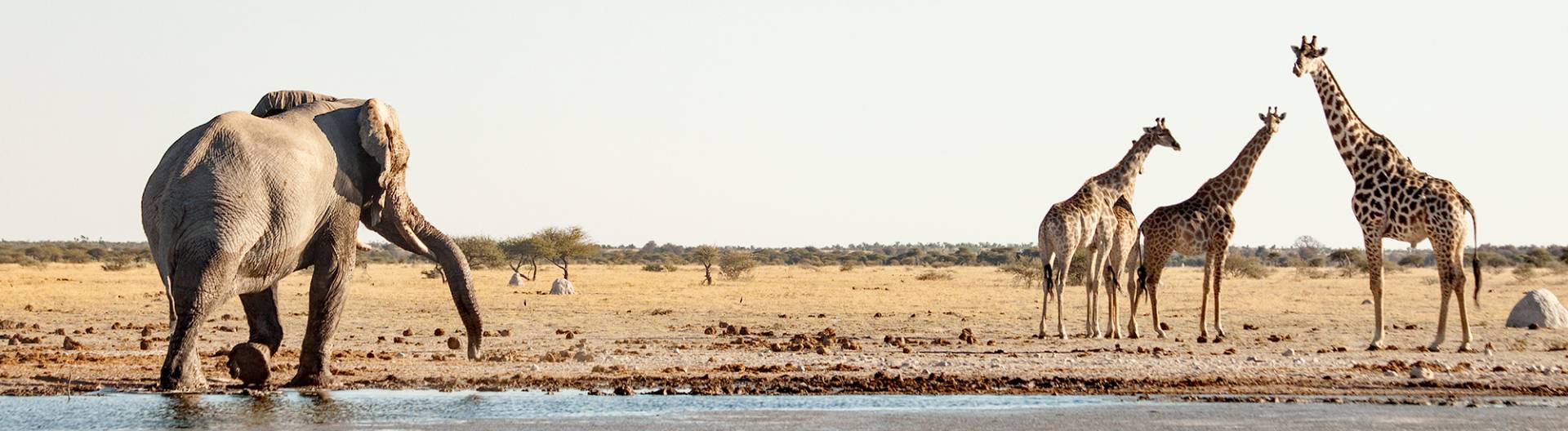
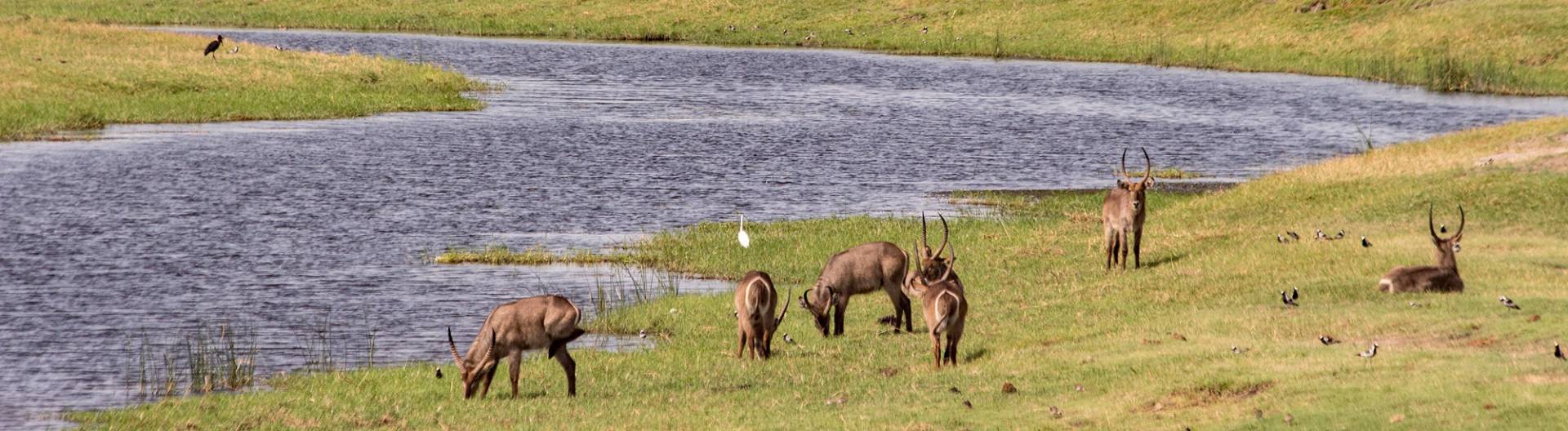
In contrast to the dry savanna areas, the world famous Okavango Delta offers an abundance of water and attracts a huge variety of wildlife. The largest inland delta in the world is considered one of the last natural paradises of the earth.
Botswanas natural regions
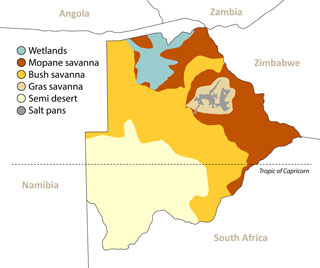
We subdivide Botswana into four natural regions (see also geographic map). This is our own simplified map, which we have assembled from different scientific maps.
A very good, complex map of the Botswana vegetation areas can be found at the European Soil Data Centre. Here is a link to the Vegetation Map of the Republic of Botswana.
The following four natural areas can be easily defined for Botswana:
- Kalahari area with semi-desert and bush savannah in the south, west and central area
- Okavango Delta and other wetlands in the north
- Tree savannah in the rainy north and east
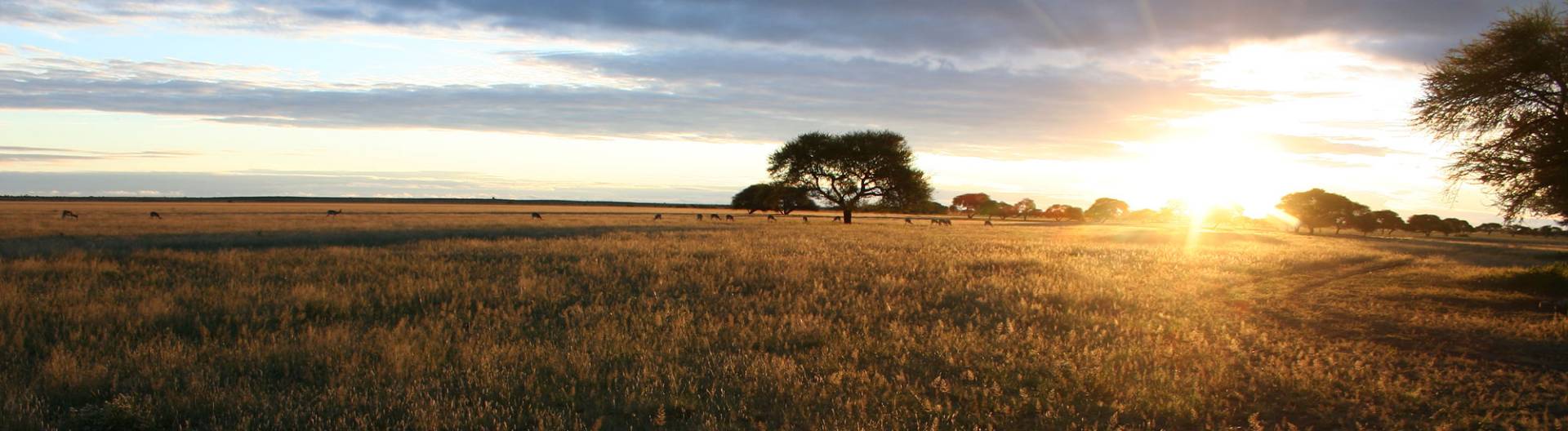
- Salt pan areas with surrounding grass savannah
1. Kalahari area with semi-desert and bush savannah
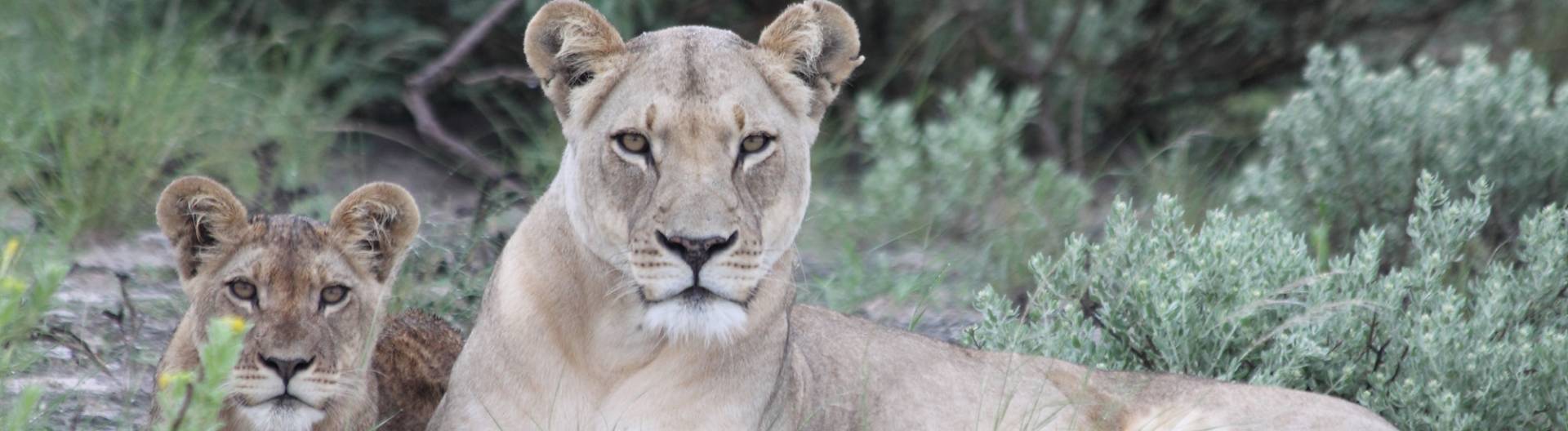
The Kalahari, with the Central Kalahari Game Reserve and the Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park National Parks, is part of the 2.5 million-square-kilometer Kalahari Bay, one of the largest contiguous sand areas on Earth. The Kalahari is often called a desert (Kalahari desert), but it is a semi-desert or bush savannah.
The Kalahari offers an abundance of wildlife life through relatively abundant rainfall. The San (Bushmen), who have been living in the Kalahari for thousands of years, know more than 1,000 plants. The Kahalari hosts a great variety of wildlife. Especially in the national parks there live countless mammal and bird species.
2. Okavango Delta and wetland region
The Okavango Delta is the largest inland delta in the world and has an area of approximately 15,000 km². In the rainy season, it grows to over 20,000 km ². In the Delta, the Okavango meets the sand savannah of the Kalahari and forms a unique connection worldwide: desert and marshland of the Delta with a fascinating flora and fauna.
Other wetlands in the north of Botswana are the Linyanti and the Kwando, which are sometimes called "small Okavango Delta" and also have a large and varied wildlife.
3. Tree savannah
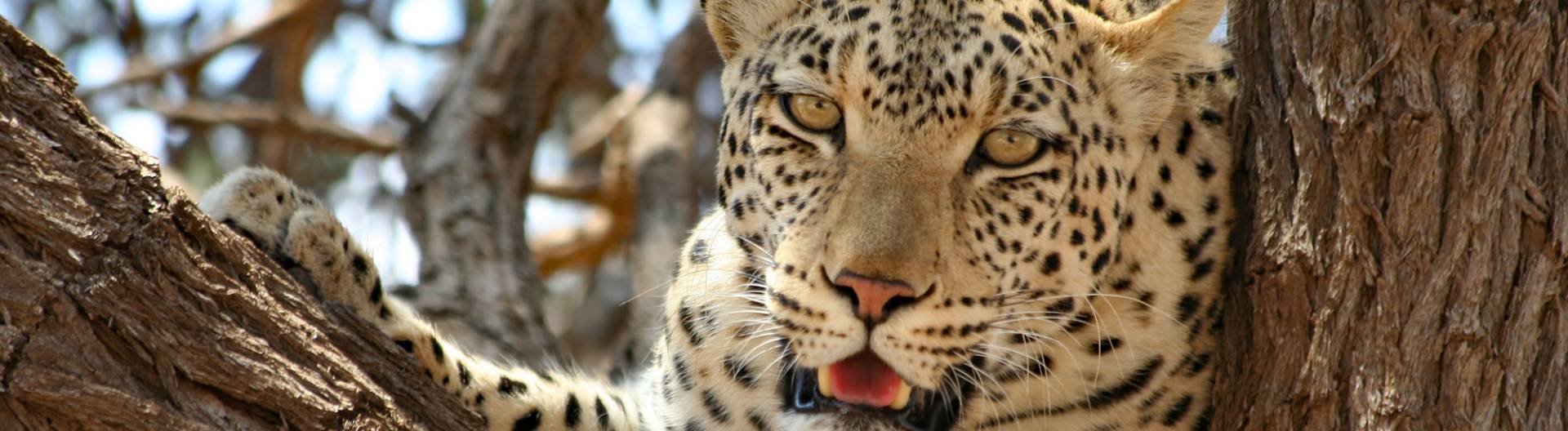
The tree savannah of Botswana is situated mainly around the Okavango Delta and further into the north and northwest. Here the Mopane tree is predominant. Every now and then, tropical tree forests occur on the rivers. Some game reserves, for example the Chobe National Park, offer ideal conditions for African big game.
In the more densely populated west of the country, especially around the capital Gaborone, there is hardly any wildlife living.
4. Pan areas with surrounding grass savanna
These are the Makgadikgadi and Nxai Pans and the surrounding savanna area. The world's largest salt pans were created by evaporation of a huge inland lake in central Botswana of about 60000 km ² extent, whose inflows were prevented by shifting of soil. Since Makgadikgadi was the deepest point, the salt concentrated here and today forms huge salt layers up to 5 m thick.
Around the salt pans lies open grassland, which is the center of attraction of the largest zebra migration outside Tanzania. During the rainy season, from December to March, large herds of zebra, oryx, wildebeest, impala and springbok are found in Nxai Pan National Park.